Hierarchy Waste Management
Hey friend! I recently came across some interesting information about waste management hierarchy, and I thought I'd share it with you. Waste management hierarchy is a system that helps prioritize waste management strategies based on their environmental impact. It promotes the idea of reducing waste at the source and managing it in the most sustainable way possible.
Epa Waste Management Hierarchy - Hierarchy Of Solid Waste Management
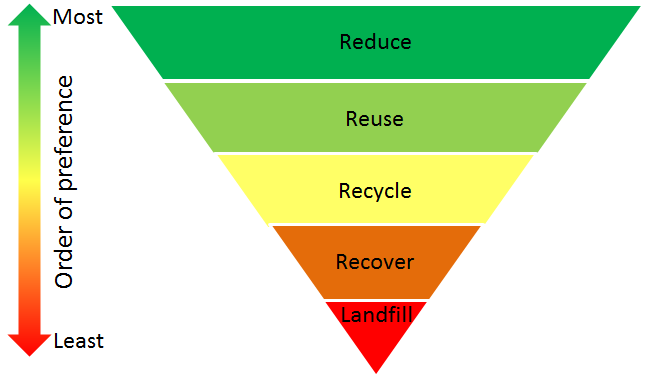
Let's start with the first image, which gives us an overview of the waste management hierarchy. You can find the image here. The image illustrates the different stages of waste management in a hierarchical order, with the most preferable methods at the top and the least preferable at the bottom.

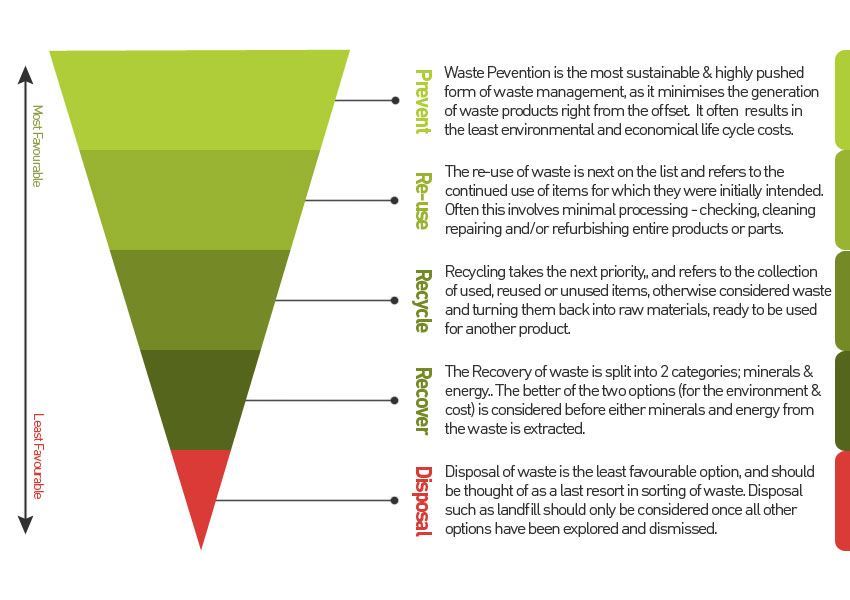
At the top of the hierarchy, we have the most preferred waste management method, which is "Source Reduction" or waste prevention. This involves taking measures to reduce the amount of waste generated in the first place. Some examples include using reusable products instead of disposable ones and buying products with less packaging.
The next level is "Reuse," which involves finding new uses for items that would otherwise become waste. For example, donating clothes or furniture instead of throwing them away or using refillable water bottles instead of single-use plastic ones.
The third level is "Recycling," where waste materials are processed and transformed into new products. Recycling helps conserve resources and reduces the amount of waste sent to landfills. It's important to separate recyclable materials from other types of waste to ensure they can be properly recycled.
The fourth level is "Energy Recovery" or "Waste-to-Energy." In this stage, non-recyclable waste is used to generate energy through processes like incineration or anaerobic digestion. This helps recover some value from waste and reduces the reliance on fossil fuels for energy production.
The last level in this hierarchy is "Disposal," which includes landfilling and incineration without energy recovery. Landfilling is the least preferable option as it can have serious environmental impacts such as groundwater contamination and the production of methane, a potent greenhouse gas. Incineration without energy recovery also has negative impacts as it releases pollutants into the air.
Waste Hierarchy - NAWMA - Northern Adelaide Waste Management Authority
Moving on to the second image, you can find it here. This image specifically represents the waste hierarchy followed by the Northern Adelaide Waste Management Authority (NAWMA).

NAWMA emphasizes the importance of waste prevention as the top priority in their waste management approach. They encourage individuals and businesses to find ways to reduce waste generation through conscious consumer choices and efficient resource utilization.
If waste prevention is not possible, NAWMA promotes the idea of reusing items whenever feasible. They encourage the community to donate or exchange items they no longer need, fostering a circular economy where resources are conserved and waste is minimized.
The third stage in NAWMA's waste hierarchy is recycling. They have implemented comprehensive recycling programs that allow residents to recycle a wide range of materials such as paper, glass, plastic, and metal. Proper sorting of recyclables is essential to ensure the materials can be effectively processed and turned into new products.
If waste cannot be prevented, reused, or recycled, NAWMA focuses on recovering energy from waste to minimize its impact on the environment. They utilize modern technologies like anaerobic digestion and incineration with energy recovery to convert waste into useful energy sources.
If all other options have been exhausted, NAWMA resorts to disposal. They have landfill facilities that are designed and managed following strict environmental guidelines to minimize the potential environmental harm associated with this waste management method.
Waste Management Hierarchy - Showing in a hierarchical order, the
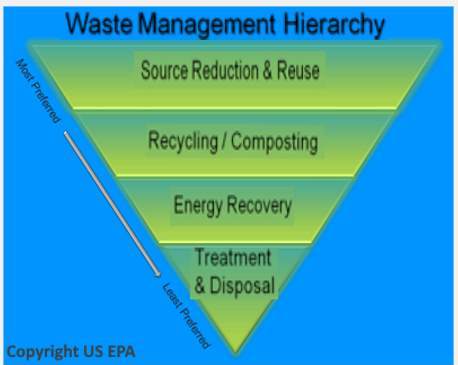
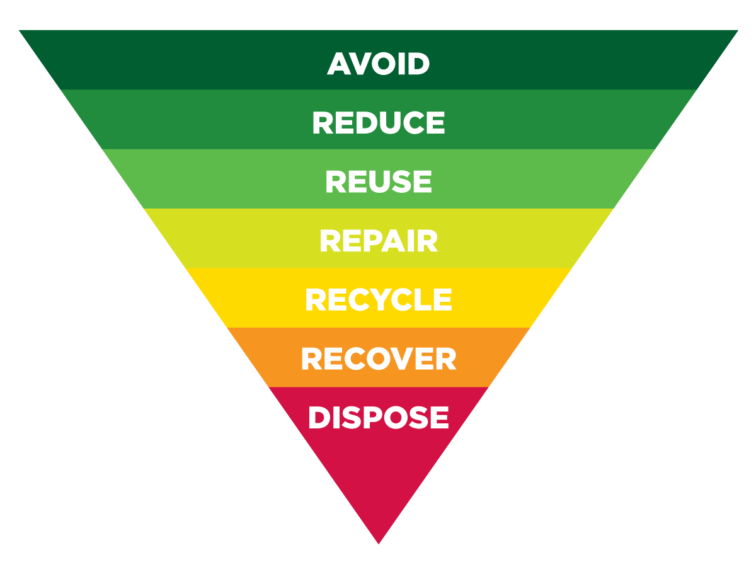
The next image gives us a more detailed look at waste management hierarchy. You can find it here. It provides a clear visual representation of different waste management approaches.

The image demonstrates that waste management follows a cascading order, with waste prevention as the most preferred option, followed by reuse, recycling, energy recovery, and finally, disposal.
Waste prevention involves reducing waste generation through practices like product design, packaging reduction, and consumer education. By minimizing waste at its source, we can significantly reduce the environmental impact associated with waste management.
If waste prevention is not possible, the next best option is reuse. This involves finding new ways to use products or materials before they become waste. It can include activities like repairing, refurbishing, or repurposing items.
The third level is recycling, where waste materials are processed to create new products or raw materials. Recycling reduces the demand for virgin materials and helps conserve natural resources. Proper sorting and separation of recyclables are essential to ensure the effectiveness of recycling programs.
If recycling is not feasible, the next level is energy recovery. This involves the conversion of waste into useful forms of energy. Technologies like incineration and anaerobic digestion are used to extract energy from waste while minimizing environmental impacts.
The last stage of waste management hierarchy is disposal, which includes methods like landfilling and incineration without energy recovery. These methods are considered the least desirable options due to their potential negative impacts on the environment. Proper management and monitoring of landfills are crucial to prevent pollution and minimize environmental hazards.
Waste management hierarchy. | Download Scientific Diagram
The fourth image provides another scientific representation of waste management hierarchy, and you can check it out here.

This image presents waste management methods in a simplified way, focusing on waste prevention as the most favorable option. It highlights the importance of reducing waste generation through practices like improving manufacturing processes, promoting sustainable consumption, and implementing waste reduction policies.
If waste prevention is not possible, the image emphasizes the need for reusing materials. It encourages individuals and organizations to find creative ways to extend the life of products and reduce the demand for new resources.
The third level is recycling, with a strong emphasis on proper waste segregation and collection to ensure recyclables are effectively processed. Recycling plays a crucial role in conserving resources, reducing energy consumption, and mitigating environmental pollution.
If recycling is not feasible, the image suggests energy recovery as an alternative. It emphasizes the need for advanced technologies that allow the extraction of energy from waste without compromising environmental integrity.
Finally, the image acknowledges disposal as the last resort, indicating the negative environmental impacts associated with landfilling and incineration. It highlights the importance of responsible waste management practices and the use of modern landfills designed to minimize pollution.
I hope you find this information helpful and informative! Waste management hierarchy is an important concept that can guide us towards more sustainable waste management practices. By prioritizing waste prevention, reuse, recycling, energy recovery, and responsible disposal, we can contribute to a healthier environment and a more sustainable future.
The waste management hierarchy (Adapted from UNEP, 2011 24 ) | Download
The next image provides us with a waste management hierarchy adapted from UNEP (United Nations Environment Programme). You can view it here.

The hierarchy depicted in this image aligns with the previous representations, emphasizing waste prevention as the most favorable option. Waste prevention involves measures taken to reduce waste generation and promote sustainable consumption patterns.
If waste prevention is not feasible, the image promotes reuse as the next preferred option. Reuse involves finding new uses for products or materials, extending their lifespan, and minimizing environmental impacts.
An important feature of this hierarchy is the concept of "Materials Recycling." It highlights the significance of recycling materials and recovering valuable resources from waste. Proper recycling practices not only conserve resources but also reduce the energy required for manufacturing new products.
The next level is "Waste-to-Energy," which represents the conversion of waste into useful forms of energy through processes like incineration or anaerobic digestion. This allows us to extract value from waste while minimizing its environmental impact.
The last stage represents disposal, involving landfilling or incineration without energy recovery. While these methods may be necessary for certain types of waste, they should be viewed as the least desirable options and should only be considered when all other avenues have been exhausted.
Reducing your Waste Costs | Direct365 Blog
Now, let's move on to the next image, which you can find here. This image focuses on reducing waste costs in waste management practices.

The image provides a simplified representation of waste management hierarchy, emphasizing cost reduction. It acknowledges that effective waste management strategies can result in significant cost savings for businesses and individuals.
At the top of the hierarchy, we have waste prevention, which is highlighted as the most cost-effective option. By focusing on reducing waste at the source, businesses can avoid unnecessary expenses associated with waste disposal and management.
The next level is waste reduction through recycling and reuse. Implementing recycling programs and finding ways to reuse materials can lead to reduced waste disposal costs, as recycling is often less expensive than landfilling or incineration.
The last level that affects costs is waste disposal. The image suggests that proper waste segregation and identification of hazardous waste can help minimize disposal costs by ensuring that waste is managed in the most appropriate and cost-effective way.
This image reminds us that waste management practices should not only focus on environmental benefits but also consider the financial implications for businesses and individuals.
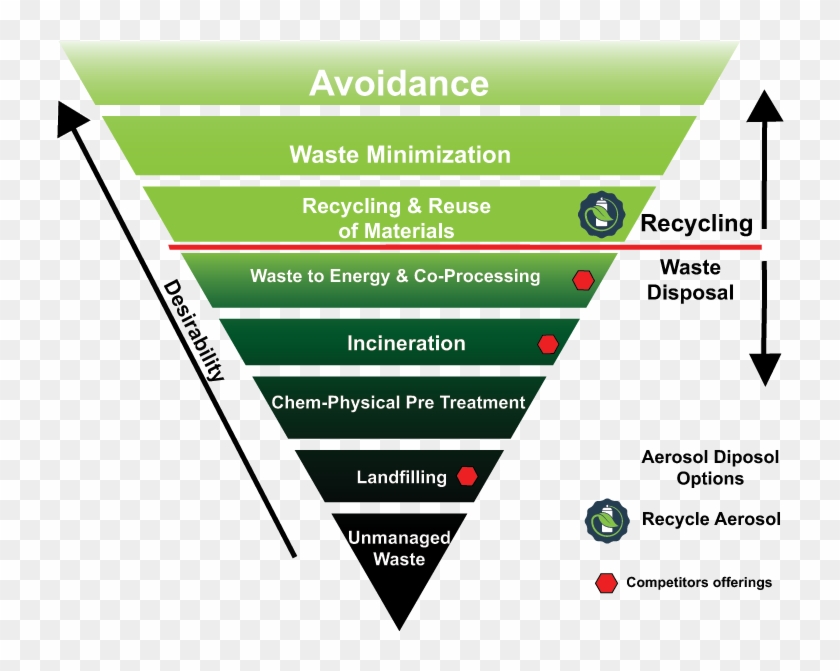
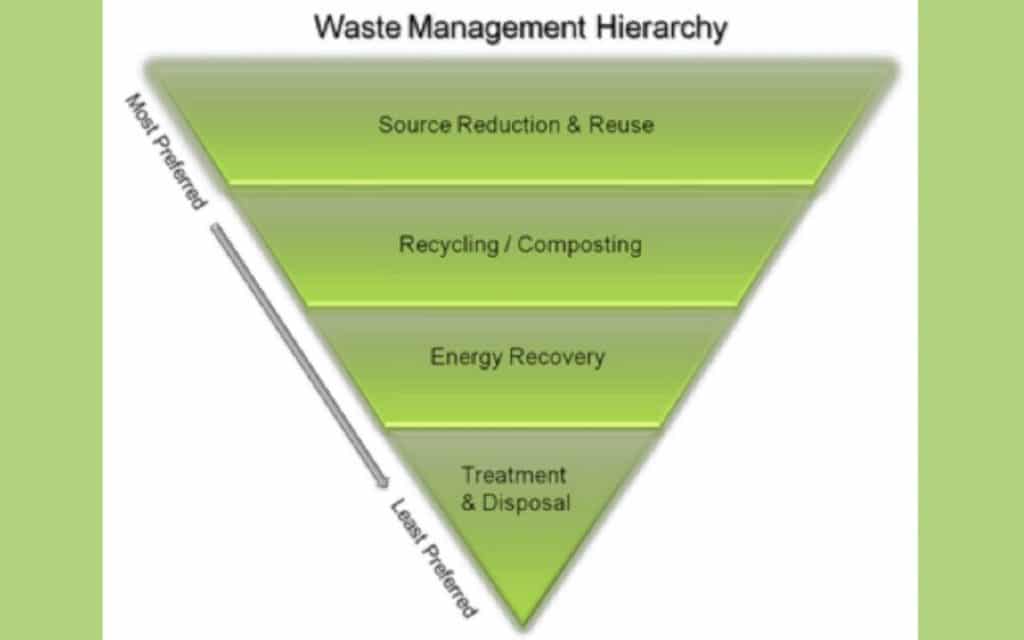
Waste Management Hierarchy - The Driver for Sustainable Biogas Development
The next image is quite interesting as it explores the role of waste management hierarchy in driving sustainable biogas development. You can find it here.

The image presents an inverted pyramid to represent the waste management hierarchy, with biogas development serving as the driver for sustainable waste management practices.
At the top of the pyramid, we have "Source Reduction," which aligns with the previous hierarchy representations. Source reduction aims to minimize waste generation and reduce environmental impacts.
The next level is "Organics Recycling," which focuses on the recycling and recovery of organic waste materials. This is where biogas development comes into play. Biogas, a renewable energy source, can be produced through the anaerobic digestion of organic waste materials. This process not only diverts waste from landfills but also generates valuable energy.
This image emphasizes the potential of biogas production in contributing to sustainable waste management. By utilizing organic waste to produce renewable energy, we can minimize environmental pollution, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and promote a circular economy.
Sustainable Solid Waste Management in India: January 2012
Now, let's take a look at the next image, which focuses on sustainable solid waste management in India. You can view it here.

This image represents sustainable waste management hierarchy specifically tailored for India. It highlights the need for a comprehensive and integrated approach to managing solid waste in the country.
The top level of the hierarchy is "Waste Minimization," which aligns with waste prevention in other representations. It focuses on reducing waste generation through initiatives like public awareness campaigns, efficient resource utilization, and sustainable consumption patterns.
The next levels include "Segregation at Source" and "Doorstep Collection," emphasizing the importance of proper waste segregation and organized collection systems. Effective segregation and collection lay the foundation for efficient waste
If you are looking for Waste Transition Plan | The Australian Greens you've visit to the right page. We have 35 Images about Waste Transition Plan | The Australian Greens like What is the Waste Hierarchy? | ISM Waste & Recycling, Waste hierarchy for construction - Designing Buildings and also Waste Management Hierarchy Steps | Hierarchy Structure. Read more:
Waste Transition Plan | The Australian Greens
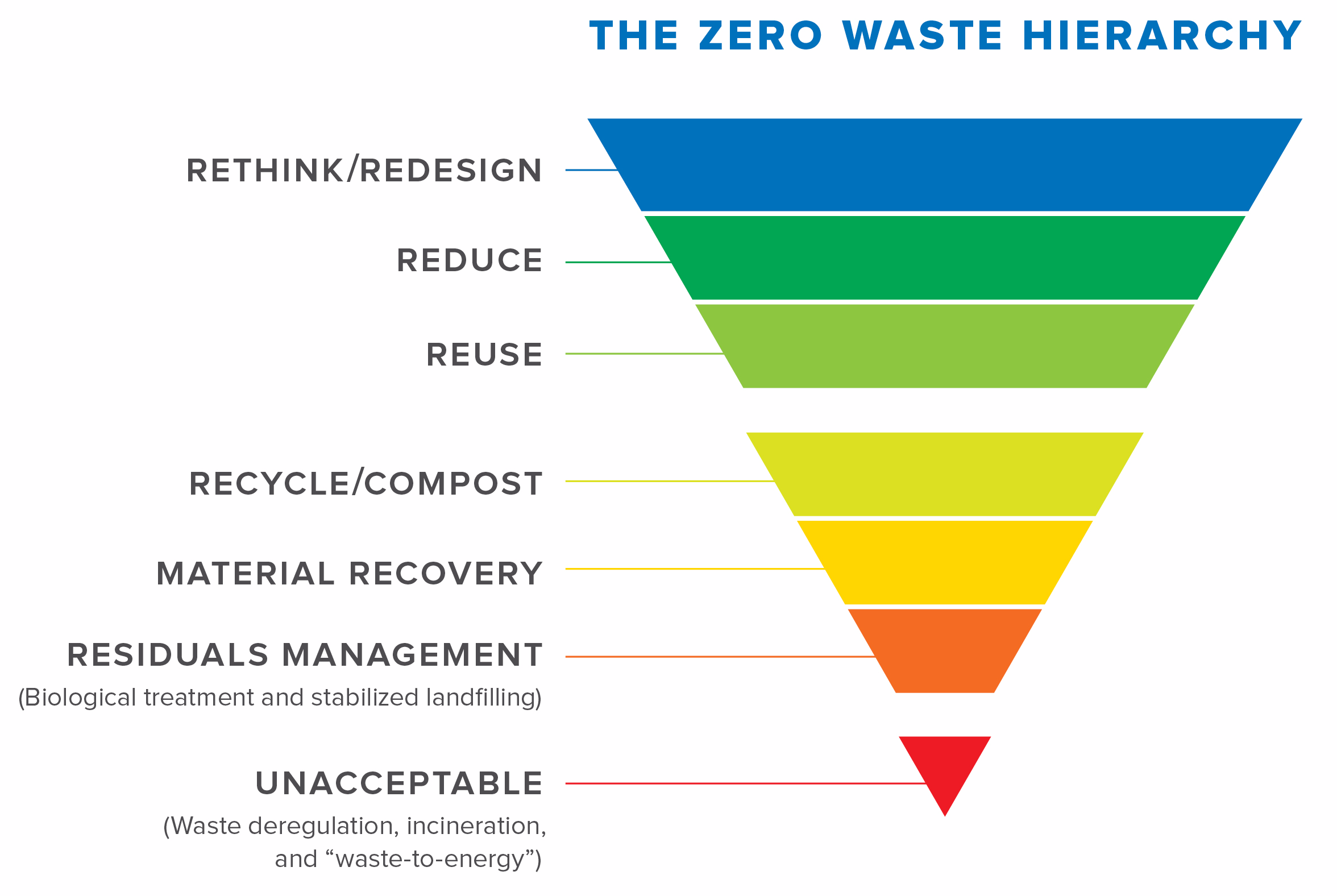 greens.org.au
greens.org.au waste hierarchy zero reduce sustainability management reuse rethink economic action social energy recycle chart system circular recycling recovery plan economy
THE WASTE MANAGEMENT HIERARCHY CONCEPT – ENVASS
 www.envass.co.za
www.envass.co.za hierarchy
The Waste Management Hierarchy (Adapted From UNEP, 2011 24 ) | Download
 www.researchgate.net
www.researchgate.net hierarchy framework directive unep decommissioning described kibii reuse
Waste Hierarchy - EMSmastery
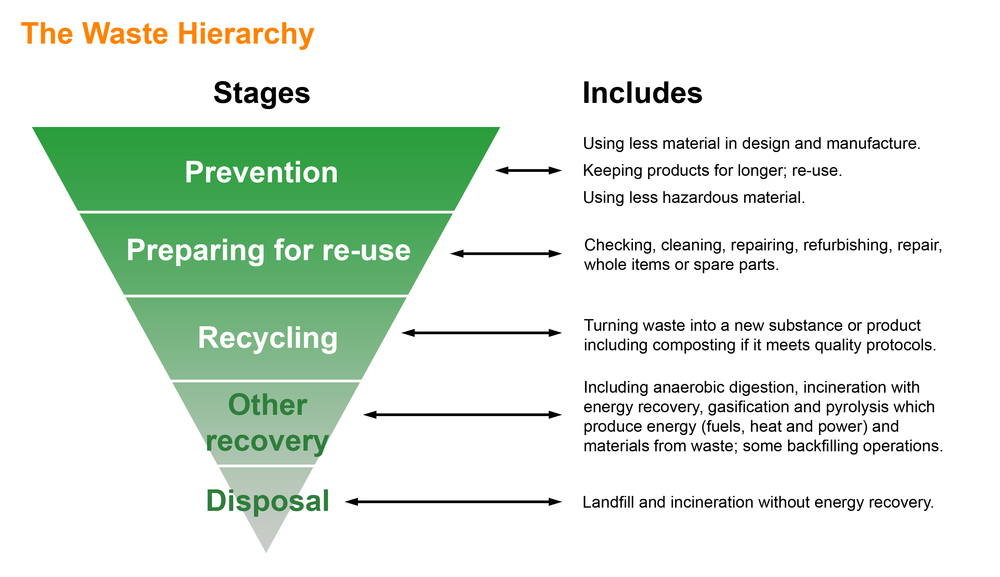 emsmastery.com
emsmastery.com hierarchy worker
Is Waste Hierarchy A Misleading Principle? – Wasteless Future
 wastelessfuture.com
wastelessfuture.com waste hierarchy principle letsrecycle
Hierarchy In Solid Waste Management. | Download Scientific Diagram
 www.researchgate.net
www.researchgate.net hierarchy
What Is The Waste Hierarchy? | ISM Waste & Recycling
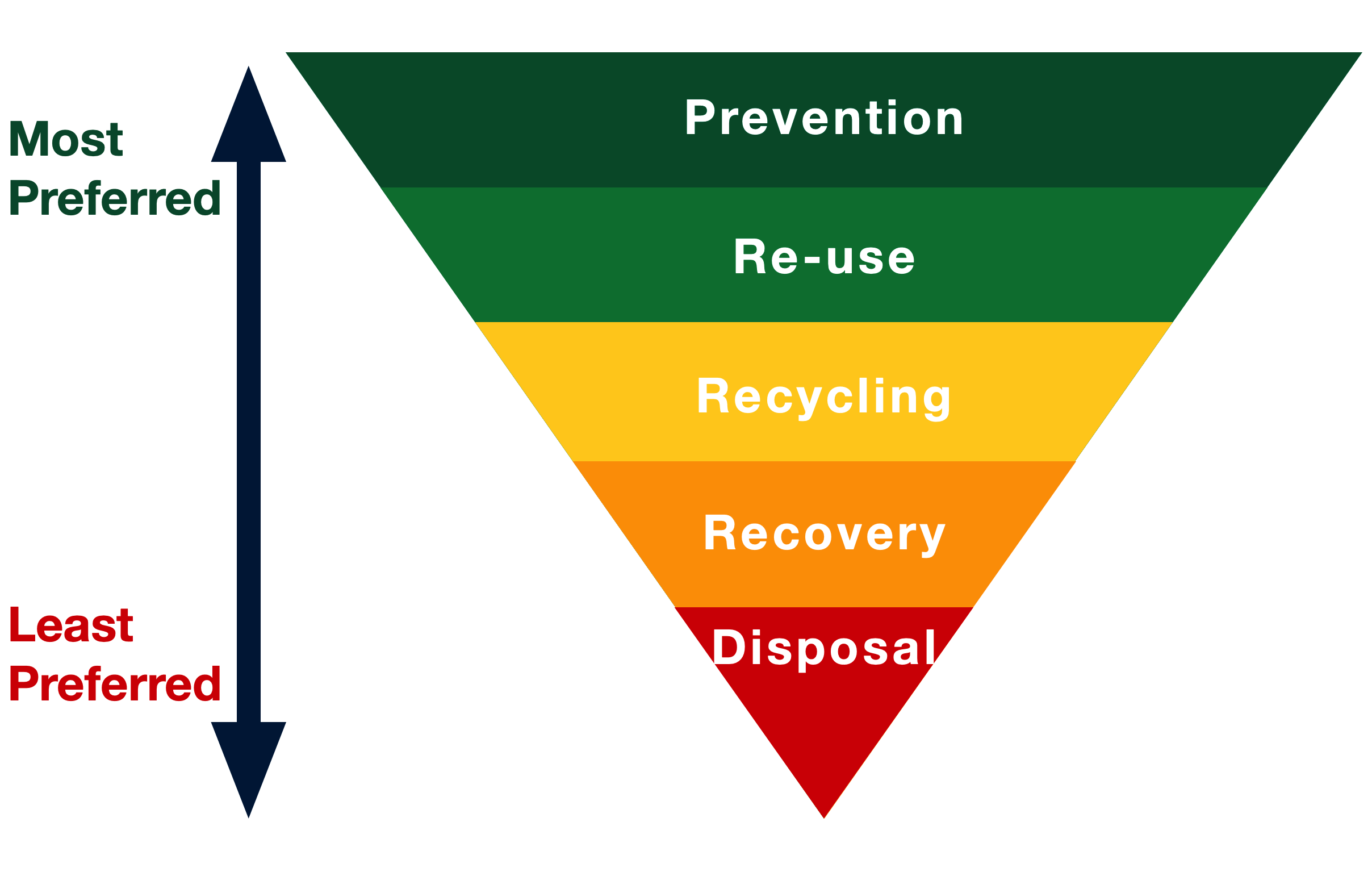 ismwaste.co.uk
ismwaste.co.uk hierarchy mean
Sustainability | ASI Comprehensive Waste Management | ASI Waste
waste hierarchy management sustainable
Waste Management Hierarchy - Bax & Company
 baxcompany.com
baxcompany.com hierarchy baxcompany
Waste Hierarchy Adapted From Directive 2008/98/EC [5]. | Download
![Waste hierarchy adapted from Directive 2008/98/EC [5]. | Download](https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Oliver_Fisher3/publication/324145647/figure/download/fig2/AS:636294304632832@1528715792107/Waste-hierarchy-adapted-from-Directive-2008-98-EC-5.png) www.researchgate.net
www.researchgate.net hierarchy directive adapted
Waste Hierarchy For Construction - Designing Buildings
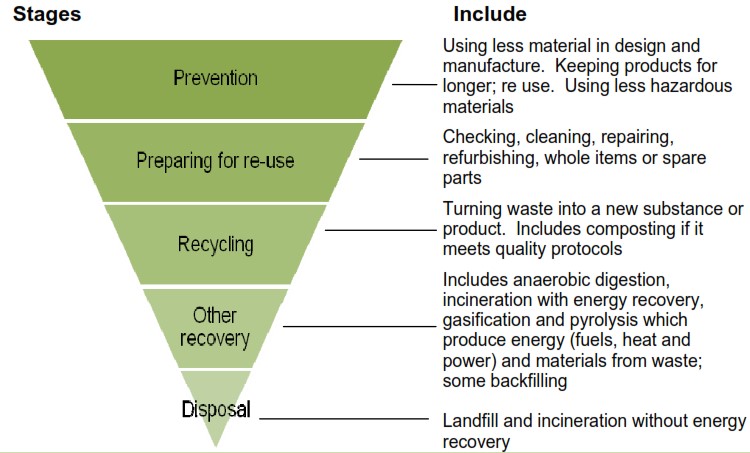 www.designingbuildings.co.uk
www.designingbuildings.co.uk waste hierarchy construction defra guidance applying union buildings bodies businesses application public
Reuse And Repair – Northern Ireland Resources Network
 www.ni-rn.com
www.ni-rn.com reuse hierarchy prevention less
Waste Management Hierarchy
 www.slideshare.net
www.slideshare.net hierarchy
Hierarchy Of Waste Management | Download Scientific Diagram
 www.researchgate.net
www.researchgate.net hierarchy
Waste - Safety Central
 safety.networkrail.co.uk
safety.networkrail.co.uk waste hierarchy safety management examples decisions prioritise some environment
Epa Waste Management Hierarchy - Hierarchy Of Solid Waste Management
 www.pngfind.com
www.pngfind.com hierarchy epa pngfind pngkit
Waste Management Hierarchy - The Driver For Sustainable Biogas Development
 anaerobic-digestion.com
anaerobic-digestion.com waste hierarchy management pyramid inverted epa diagram sustainable digestion anaerobic priorities biogas development making driver
Waste Management Hierarchy - Bax & Company
 baxcompany.com
baxcompany.com hierarchy waste
Waste Management Hierarchy Steps | Hierarchy Structure
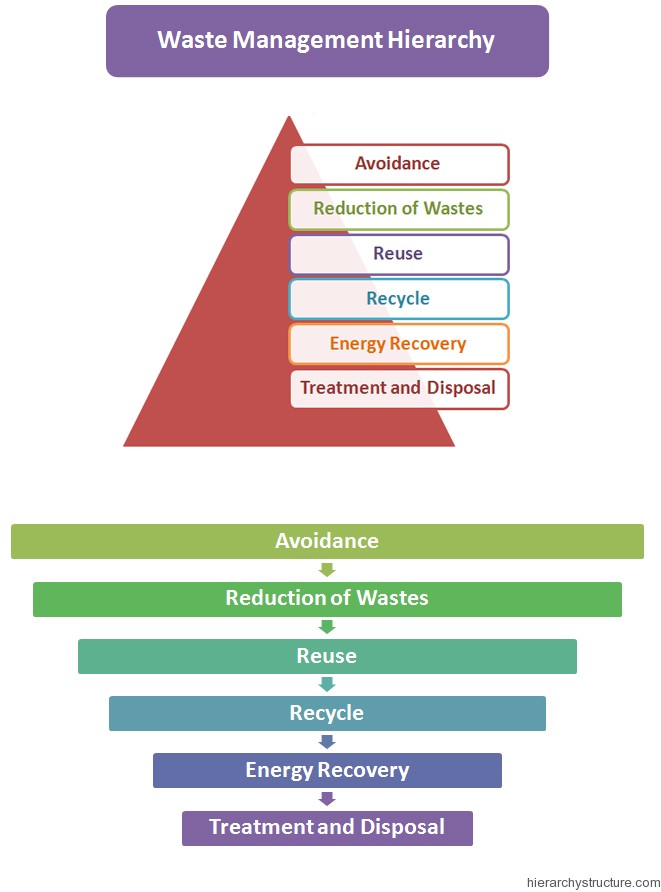 hierarchystructure.com
hierarchystructure.com waste management hierarchy reduction disposal avoidance steps structure reuse treatment
Waste Hierarchy - PROSINO Shredder And Granulator
waste hierarchy disposal
Hierarchy Of Waste Management [27]. | Download Scientific Diagram
![Hierarchy of waste management [27]. | Download Scientific Diagram](https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Samuel-Fosu-Gyasi/publication/339721118/figure/download/fig2/AS:865715594739712@1583414090370/Hierarchy-of-waste-management-27.png) www.researchgate.net
www.researchgate.net hierarchy waste
Waste Hierarchy - NAWMA - Northern Adelaide Waste Management Authority
 www.nawma.sa.gov.au
www.nawma.sa.gov.au waste hierarchy partnerships
What Is The Waste Hierarchy? – Sadlers
 sadlers.co.uk
sadlers.co.uk waste hierarchy recycling let detail look these
Reducing Your Waste Costs | Direct365 Blog
 www.direct365.co.uk
www.direct365.co.uk hierarchy reducing direct365
What Is The Waste Hierarchy? Waste Hierarchy Explained | ETM Recycling
 www.recyclingbristol.com
www.recyclingbristol.com waste hierarchy explained
The Waste Management Hierarchy [2] | Download Scientific Diagram
![The Waste Management Hierarchy [2] | Download Scientific Diagram](https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Shahnoza_Boboeva/publication/315829858/figure/download/fig1/AS:481085046956032@1491711021487/The-Waste-Management-Hierarchy-2.png) www.researchgate.net
www.researchgate.net waste hierarchy
ILSR Food Waste Recovery Hierarchy - We Hate To Waste
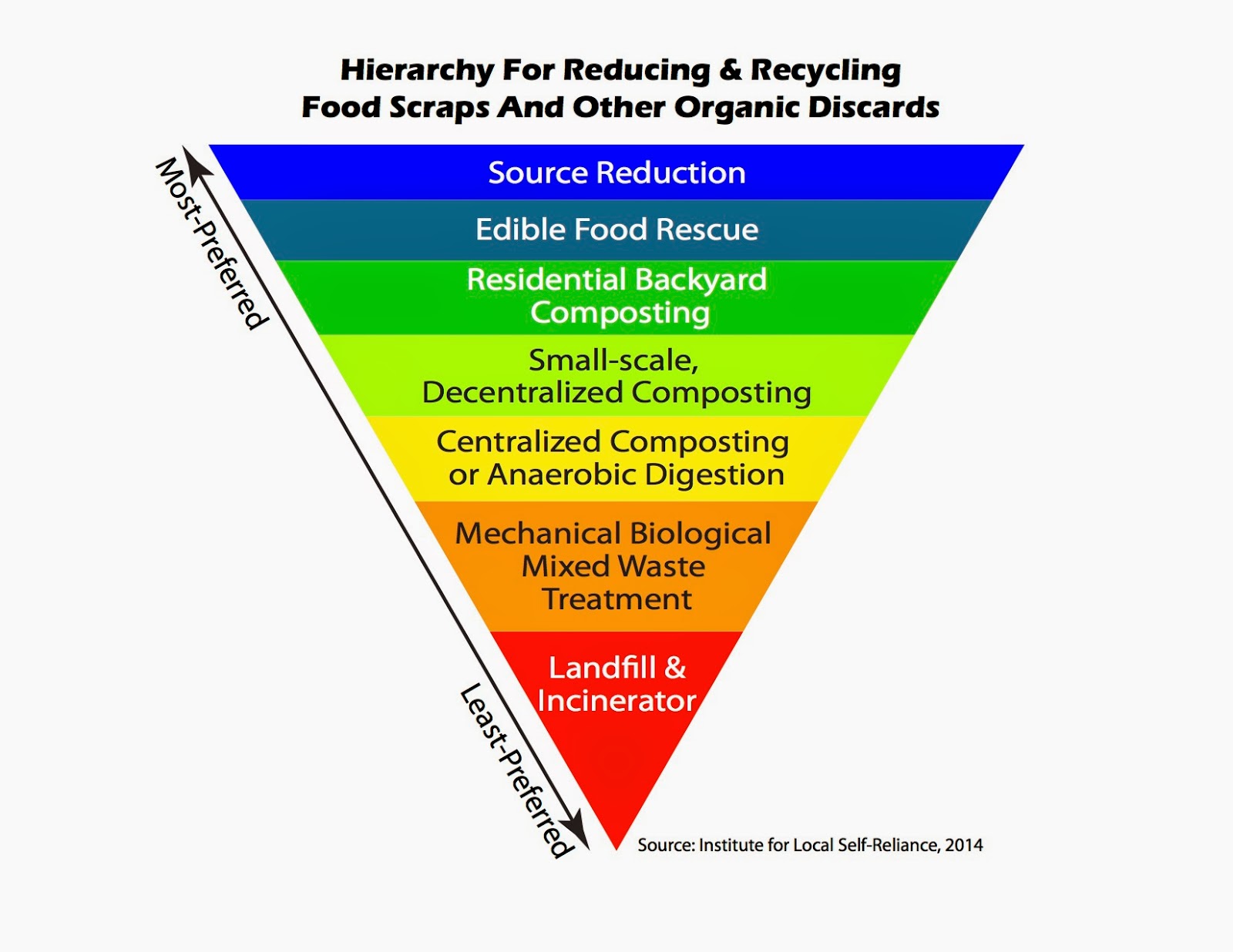 www.wehatetowaste.com
www.wehatetowaste.com hierarchy recovery ilsr bioenergy biowaste zerowasteeurope
The Waste Hierarchy – Reuse Is The New Recycling — Children's Scrapstore
 www.childrensscrapstore.co.uk
www.childrensscrapstore.co.uk waste hierarchy reuse recycling food
Environment,Health, Safety: WASTE MANAGEMENT HIERARCHY
 ehsnewsindia.blogspot.com
ehsnewsindia.blogspot.com hierarchy
Waste Management Hierarchy -Showing In A Hierarchical Order, The
 www.researchgate.net
www.researchgate.net hierarchy hierarchical sustainable
Timo Rissanen: Fashion Creation Without Fabric Waste Creation: Waste
 zerofabricwastefashion.blogspot.com
zerofabricwastefashion.blogspot.com waste hierarchy management creation rissanen timo fabric without fashion wikipedia
Business Compliance Of Waste Management - Aussie Metal Management
 aussiemetalmanagement.co.uk
aussiemetalmanagement.co.uk waste management hierarchy compliance business aussie metal uncategorized mar comments
Sustainable Solid Waste Management In India: January 2012
 swmindia.blogspot.com
swmindia.blogspot.com waste hierarchy management sustainable india recycling solid municipal composting generate electricity industrial used developing figure swm countries energy
Waste Management: Principles, Methods And Benefits | Earth Reminder
 www.earthreminder.com
www.earthreminder.com methods hierarchy disposal wastes disposing incineration landfills further
Waste Management Hierarchy. | Download Scientific Diagram
 www.researchgate.net
www.researchgate.net hierarchy
Waste hierarchy safety management examples decisions prioritise some environment. Methods hierarchy disposal wastes disposing incineration landfills further. Waste hierarchy zero reduce sustainability management reuse rethink economic action social energy recycle chart system circular recycling recovery plan economy
Comments
Post a Comment